Key Components of Efficient Automated Liquid Handling Workstations

Lab technicians measure, dispense, and mix liquids every day. Liquid handling is a key element of scientific research in various industries, from microbiology to food
Advantages of Lab-Quality Devices That Measure pH

Studying Microbe Colonies Are you curious about what pH probes measure, why pH is important, and how devices that measure pH work? In high school
Why Are Colonies Important in the Study Of Microbiology
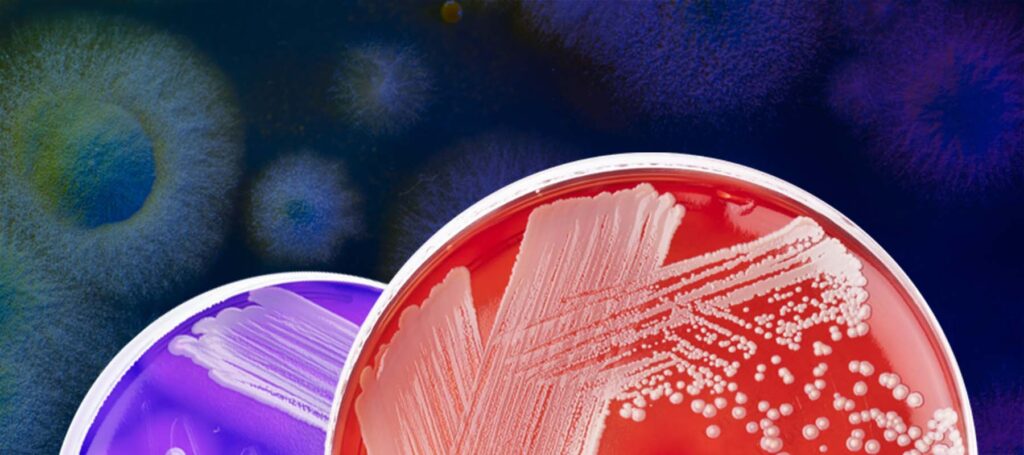
Colonies give scientists information about a particular microbe that has replicated into a group sharing the same genes. Studying that group of microbes helps microbiologists
Best Types of pH Meters for Microbiology Labs

pH is critical to life. In fact, for lifeforms living in liquids, such as the ocean, the pH of that liquid dictates what species can
Core Laboratory Automation Products for an Efficient Lab Workflow

Scientists have long sought ways to maximize their laboratory throughput by developing machinery that simplifies difficult or repetitive tasks. The use of laboratory automation products
Uses Of An Automated Liquid Dispenser In The Laboratory

Components of a pH Meter In 1961, J.J. Rodriguez of Berkeley, California, introduced a patent for an “improved buret.” He designed it to dispense liquids
How to Use a pH Meter

If you remember those science experiments from school where you used litmus paper to test solutions, you probably know what pH is. In essence, it’s
Definition of Transformation in Biology
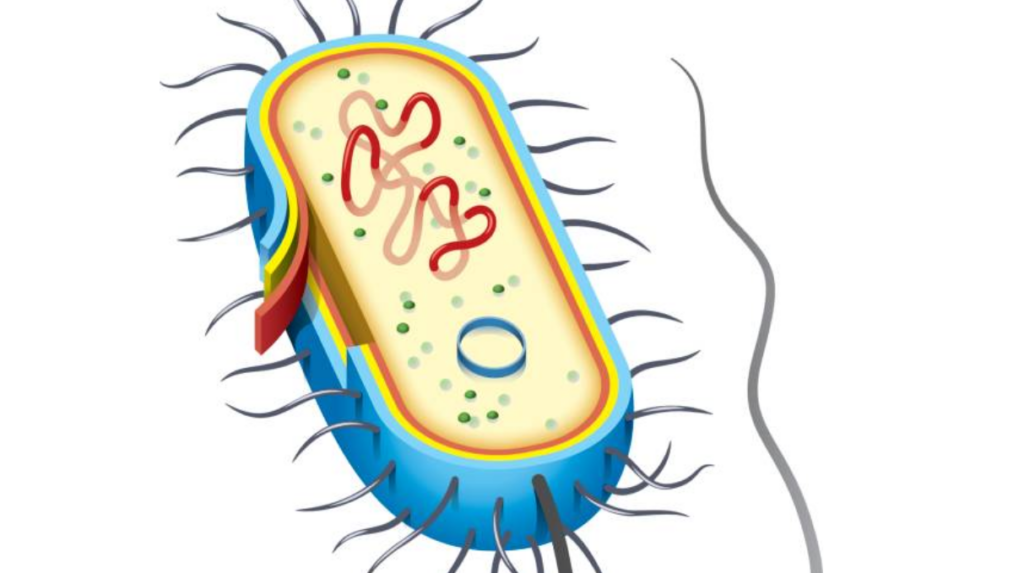
Transformation is an important component of molecular genetics; studies into the process began in the 1920s when a physician named F. Griffith realized that Streptococcus
Three Secrets to High Quality pH Meter Readings
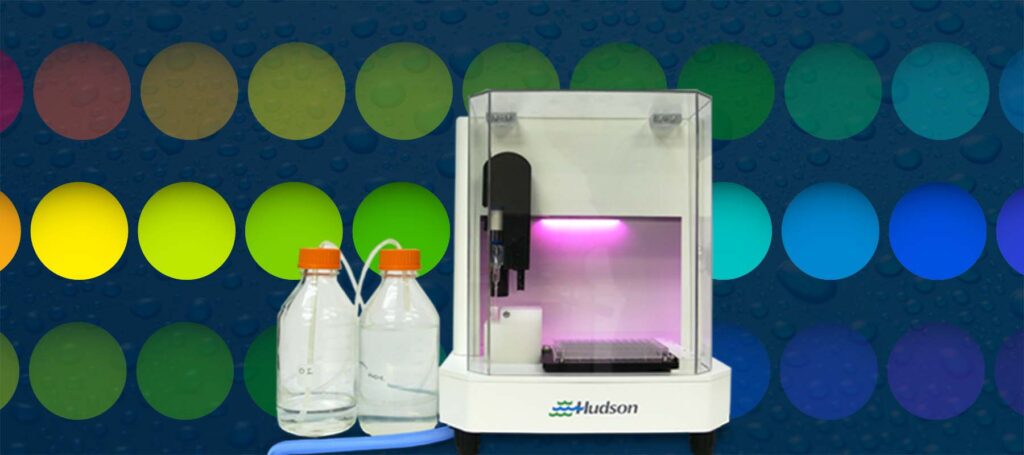

The goal of any pH reading, whether with a manual or an automated pH meter, should always be to obtain high quality pH meter readings.
Why Use A Fully Automated ELISA Reader?
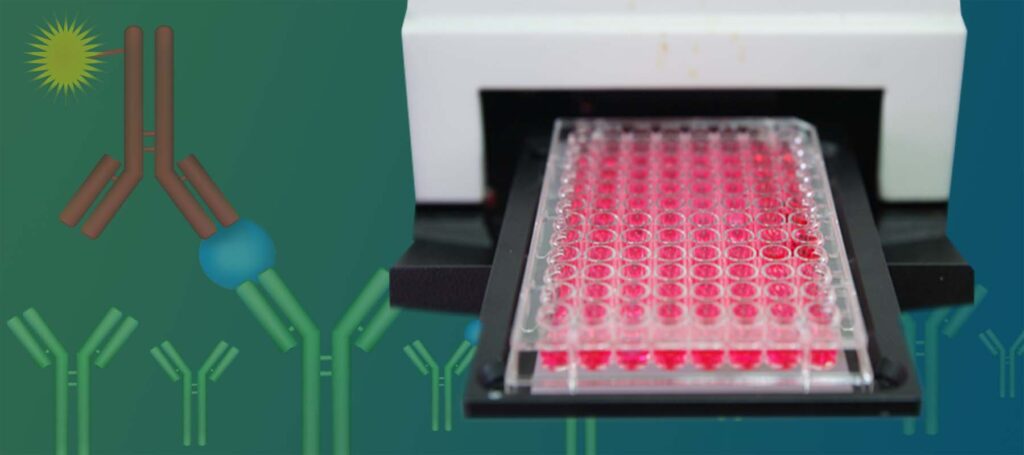

ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. It is an immunological assay that is most often used to detect and quantify proteins, antibodies/antigens, viruses, bacteria, and
